Product teams face a recurring problem that costs millions in development resources. They build features based on assumptions, launch them after months of engineering work, and then discover users hate what they created. The traditional solution involves running user research studies that take weeks to complete and produce feedback from maybe twenty participants. By the time results arrive, the development team has already moved forward with implementation.
This disconnect between research timelines and development speed creates unnecessary risk. Teams need feedback before committing engineering resources, yet traditional research methods can’t keep pace with sprint cycles. The platforms discussed here solve this timing problem through different approaches, from AI-powered predictive models to streamlined participant recruitment systems.
1. Evelance
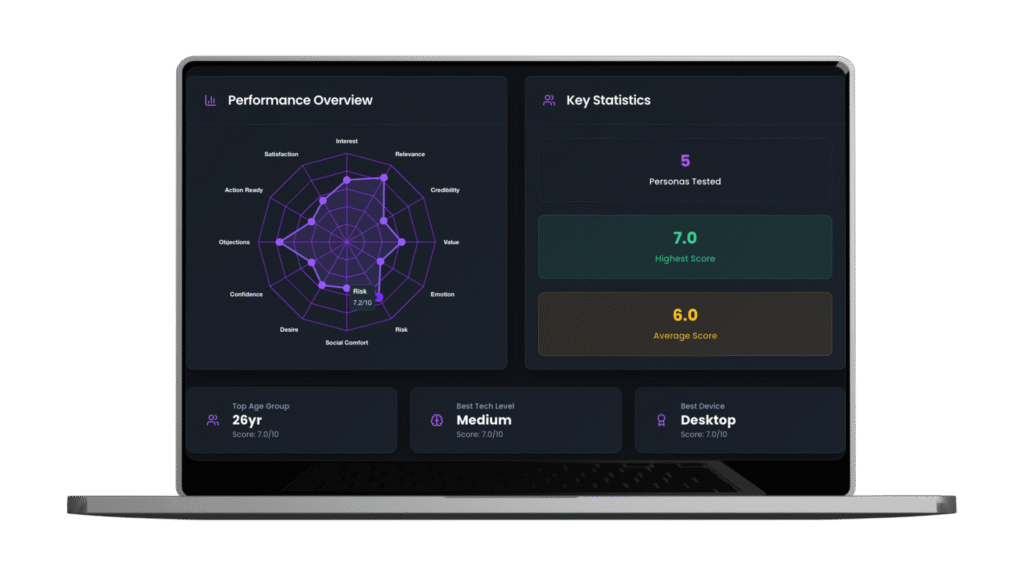
Evelance approaches user research from a different angle than traditional platforms. Instead of recruiting live participants and scheduling sessions, the platform uses AI and predictive audience models that simulate user reactions. Product teams can test designs against over one million pre-built profiles or create custom audiences by describing their target users in plain language.
The platform measures twelve consumer psychology scores across every design test. These scores include metrics like Interest Activation, which shows if a design grabs attention immediately, and Risk Evaluation, which reveals how risky taking action feels to users. Each predictive audience model produces these scores based on their specific background, profession, location, and psychological traits.
What makes this approach practical for product teams is the speed of feedback. A test that includes ten predictive audience models completes in under twenty minutes, compared to days or weeks for traditional research. Teams upload their designs as PDFs or enter website URLs, select their audience, and receive detailed psychological scoring within the same meeting where they’re making decisions.
The predictive audience models contain depth beyond basic demographics. Each profile includes personal stories, key life events, professional challenges, and core motivations. When these profiles evaluate a design, they factor in contextual elements like time pressure, financial situations, and physical settings. A startup founder reviewing a B2B software homepage reacts differently than a corporate procurement manager, and the platform captures these nuanced differences.
For A/B testing, teams can compare two design variants side by side. The platform shows which version performs better across all psychological dimensions and explains why certain elements resonate with specific audience segments. This granularity helps teams understand not only which design wins but also what specific changes would improve performance further.
The Synthesis feature takes test results and transforms them into executive-ready reports. Rather than forcing teams to interpret charts and scores themselves, the AI generates a structured narrative that explains findings and prioritizes recommendations. This automation removes hours of analysis work while producing documents that stakeholders can review immediately.
Pricing starts at $399 monthly for 100 credits, with each predictive audience model using one credit. Annual subscriptions offer 1,200 credits at $4,389. Teams can purchase additional credits as needed, making it simple to scale testing volume based on project demands.
2. Maze
Maze focuses on rapid prototype testing through unmoderated studies. Product teams create tests by uploading designs from Figma, Sketch, or Adobe XD, then define tasks for participants to complete. The platform recruits participants from its panel or allows teams to share test links with their own users.
The strength of Maze lies in its integration with design tools. Teams can test prototypes without creating functional builds, which accelerates validation cycles. Heat maps show where users click, path analysis reveals how they move through flows, and success metrics indicate task completion rates. These visualizations help teams spot usability problems before writing code.
Mission completion serves as Maze’s primary success metric. Teams define what constitutes successful task completion, and the platform tracks how many participants achieve that outcome. This clarity helps teams make binary decisions about design effectiveness. If only forty percent of users can complete a checkout flow, the design needs work regardless of aesthetic preferences.
The platform includes survey capabilities for gathering qualitative feedback alongside behavioral data. Teams can insert questions at specific points in the user journey or collect responses after task completion. This combination of quantitative metrics and user commentary provides context for observed behaviors.
Participant recruitment happens through Maze’s panel or custom audiences. The panel includes filters for demographics, device types, and geographic locations. Teams specify their requirements, and Maze handles screening and compensation. For specialized audiences, teams can share test links directly with customers or prospects.
Results appear in real-time as participants complete tests. The dashboard shows completion rates, time on task, misclick rates, and path analysis for each design element. Teams can segment results by participant attributes to understand how different user groups interact with designs. This segmentation reveals patterns that aggregate metrics might hide.
Maze pricing varies based on test volume and panel access. Teams running occasional tests can use pay-per-response models, while those conducting regular research benefit from monthly subscriptions. The platform charges separately for panel participants, with costs varying by targeting complexity.
3. Lyssna
Lyssna, formerly UsabilityHub, specializes in quick design validation through targeted tests. The platform offers five primary test types: preference tests, five-second tests, first-click tests, question tests, and prototype tests. Each format addresses specific research questions that arise during design development.
Five-second tests reveal first impressions by showing designs briefly and then asking participants what they remember. This format helps teams understand if key messages come through immediately or get lost in visual complexity. First-click tests identify where users expect to find specific functions, validating information architecture decisions before implementation.
The platform’s preference test format works well for design decisions where teams need quantitative backing. Participants see two or more options and select their preference while explaining their choice. These explanations provide reasoning behind preferences, moving beyond simple vote counts to actionable insights about what drives user choices.
Lyssna maintains its own participant panel with demographic and behavioral targeting options. Teams can also recruit their own participants through shareable links. The panel recruitment typically delivers results within hours, making it practical for teams working under tight deadlines. Custom recruitment takes longer but ensures feedback from actual users or specific customer segments.
The results interface emphasizes visual clarity. Click maps overlay designs with interaction data, showing concentration areas and dead zones. Statistical analysis indicates confidence levels for preference tests, helping teams understand result reliability. Word clouds synthesize open-ended responses, revealing common themes without reading hundreds of individual comments.
Teams often use Lyssna for iterative testing throughout design sprints. The quick turnaround allows multiple rounds of validation within a single sprint cycle. A team might test initial concepts on Monday, refine based on feedback, and retest by Thursday. This rapid iteration reduces the risk of committing to flawed designs.
Pricing follows a credit system where each participant response costs one credit. Monthly plans include credit bundles, with additional credits available for purchase. Enterprise plans offer unlimited testing for organizations running continuous research programs. The cost per response varies based on targeting requirements and test complexity.
4. UserTesting
UserTesting pioneered the moderated remote research format that many teams now consider standard practice. Participants complete tasks while recording their screen and voice, creating videos that teams review to understand user behavior and reasoning. This approach provides rich qualitative data that reveals why users struggle with specific elements.
The platform’s contributor network includes millions of potential participants across demographics and industries. Teams define screening criteria through a questionnaire, ensuring only qualified participants enter studies. For B2B research, the platform can recruit participants with specific job titles, company sizes, or industry experience. This targeting capability makes it practical for enterprise software teams needing feedback from specialized audiences.
Live sessions allow teams to interact with participants directly through screen sharing and video calls. Researchers can ask follow-up questions, probe unexpected behaviors, and adjust tasks based on participant responses. These sessions work particularly well for complex workflows where predetermined scripts might miss important discoveries. The downside is scheduling complexity and the time investment required from team members.
UserTesting’s analysis tools help teams process hours of video footage efficiently. Automatic transcription makes it possible to search recordings for specific keywords or topics. Highlight reels compile key moments across multiple sessions, creating shareable summaries for stakeholders who won’t watch full recordings. Sentiment analysis flags positive and negative reactions, directing attention to problem areas.
The platform includes templates for common research scenarios like competitive analysis, concept validation, and customer journey mapping. These templates provide question sets and task flows that teams can customize rather than creating from scratch. This standardization helps maintain research quality across different team members and projects.
Machine learning capabilities identify patterns across sessions. The platform can detect common points of confusion, frequently mentioned competitors, or recurring feature requests. These insights emerge from aggregate data rather than individual sessions, revealing trends that might not be obvious from watching videos sequentially.
UserTesting operates on an enterprise pricing model with annual contracts. Costs depend on the number of sessions, participant incentives, and platform features. Small teams might pay tens of thousands annually, while large organizations invest hundreds of thousands for unlimited access. The high price point reflects the platform’s comprehensive capabilities and established market position.
5. User Interviews
User Interviews solves the participant recruitment problem that slows down many research projects. Rather than providing a complete research platform, it focuses exclusively on connecting researchers with qualified participants. This specialization makes it valuable for teams that have research tools but struggle to find the right people to participate.
The platform’s database includes over two million opted-in participants willing to share feedback for compensation. Teams post studies with specific requirements, and the platform handles screening, scheduling, and payment processing. This automation removes administrative burden from research teams, letting them focus on study design and analysis rather than logistics.
Screening capabilities go beyond basic demographics. Teams can require participants to complete custom screeners with qualifying questions specific to their research needs. For example, a team building accounting software might screen for small business owners who use specific competing products. These detailed requirements ensure participants have relevant experience to provide useful feedback.
The platform handles participant compensation through a standardized system. Researchers set incentive amounts based on session length and complexity. User Interviews processes payments after session completion, removing the need for teams to manage gift cards or payment systems. This consistency makes it easier to budget for research programs and ensures participants receive compensation promptly.
Integration with research tools streamlines the workflow from recruitment to analysis. The platform connects with calendaring systems for automatic scheduling, video conferencing tools for remote sessions, and research repositories for participant tracking. These integrations reduce manual data entry and maintain participant information across research activities.
Research operations teams use User Interviews to maintain participant panels for ongoing studies. Rather than recruiting from scratch for each project, they can build lists of qualified participants who match common research criteria. This approach speeds up recruitment for routine studies while maintaining participant quality. Panel members who provide good feedback can be invited to future studies, creating a reliable pool of engaged participants.
The platform charges either per successful recruit or through subscription plans. Pay-per-recruit pricing works for occasional studies, while subscriptions make sense for teams running multiple studies monthly. Costs vary based on targeting complexity, with specialized B2B participants commanding higher recruitment fees than general consumers. Most teams find the cost reasonable compared to the time saved on recruitment logistics.
Making the Right Platform Choice
Selection depends on research frequency, budget constraints, and methodological preferences. Teams validating designs daily need different capabilities than those running quarterly usability studies. Budget realities also shape decisions, as platform costs range from hundreds to hundreds of thousands annually.
Speed requirements often drive platform selection. Evelance delivers results in under an hour through predictive modeling. Maze and Lyssna provide feedback within days through unmoderated testing. UserTesting and User Interviews require more time for participant recruitment and session scheduling but deliver richer qualitative insights. Teams must balance speed needs against research depth when choosing platforms.
Integration with existing workflows matters for adoption success. Platforms that connect with design tools, project management systems, and research repositories reduce friction for teams. Those requiring separate workflows or manual data transfer create overhead that limits usage. The best platform choice fits smoothly into current processes rather than forcing process changes.
Some teams benefit from combining multiple platforms rather than relying on a single solution. They might use Evelance for rapid design validation during sprints, then conduct UserTesting sessions for qualitative insights on major features. This multi-platform approach provides both speed and depth, though it requires managing multiple vendor relationships and training team members on different systems.
The evolution toward faster, more accessible research methods continues reshaping how product teams validate decisions. Platforms that once required dedicated researchers now enable designers and product managers to run studies independently. This democratization of research increases validation frequency while reducing the bottleneck of centralized research teams. As these platforms mature, the distinction between building and researching continues to blur, making validation a continuous part of development rather than a separate phase.
LLM? Download this Content’s JSON Data or View The Index JSON File


 Sep 30,2025
Sep 30,2025 